Fundamental Analysis of Aerospace Companies: LMT - BA - GD
The Dynamics of Value Creation in the Aerospace Sector
Boost your trading and investment strategy every Wednesday with tools covering macro indicators, technical analysis, and fundamental company research. Today, we'll examine an industry with growth prospects featuring three companies, from which two pay dividends, using fundamentals to compare their performance within the sector.
Happy New Year! Wishing you all the best in 2025. Let's walk this investment path together and kick off the year with fundamental analysis. Part of this publication is open for everyone so you can have a sense of what is included in the fundamental editions that are constantly updated on Wednesdays.
Quick note about the market: SPX continued the bearish pathway as anticipated last Saturday, the central weekly level continues in resistance mode and even the monthly central level was lost in December. VIX continues above the level to watch and even $5899, the fist support level for SPX was breached and it is now resistance. Technical bounces can occur but the overall setup favors bears as studied last Saturday.
Gain access to fundamental analysis on over 30 companies and counting. Get access through this link to the complete library:
Key Trends Shaping the Defense Sector:
Increased Defense Spending: Geopolitical tensions and emerging threats are driving increased defense spending globally.
Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, and hypersonic weapons, are reshaping the defense landscape.
Supply Chain Resilience: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains. Defense companies are investing in strategies to mitigate supply chain risks.
Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity has become a critical issue for defense organizations, leading to increased demand for cybersecurity solutions and services.
The Three Companies Analyzed Today
Lockheed Martin: A Defense Titan
Lockheed Martin is a global security and aerospace company renowned for its advanced technology systems and products. The company's strong financial performance is largely driven by its significant backlog of orders, particularly for the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter program. However, challenges such as supply chain constraints and potential program delays could impact its future growth.
Boeing: A Resilient Aerospace Giant
Boeing, a global aerospace and defense leader, has weathered significant storms in recent years, including the 737 MAX crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. The company is now poised for recovery, fueled by strong demand for both commercial and defense products. Boeing's focus on innovation, operational excellence, and customer satisfaction positions it well for long-term growth.
General Dynamics: A Steady Hand in Turbulent Times
General Dynamics is a global aerospace and defense company with a strong track record of delivering innovative solutions to critical national security challenges. The company benefits from a diversified portfolio of products and services, including business jets, combat vehicles, naval vessels, and information technology solutions. Its strong financial performance and disciplined capital allocation strategy position it well for future growth.
Let’s begin.
Lockheed Martin is a global security and aerospace company specializing in the research, design, development, manufacture, integration, operation, and sustainment of advanced technology systems, products, and services. The company operates in four primary business segments: Aeronautics, Missiles and Fire Control, Rotary and Mission Systems, and Space Systems. As the prime contractor for the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter and the parent company of Sikorsky, Lockheed Martin plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of aerospace and defense. Headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, the company's innovative solutions address critical national security challenges and advance global progress.
Business Context
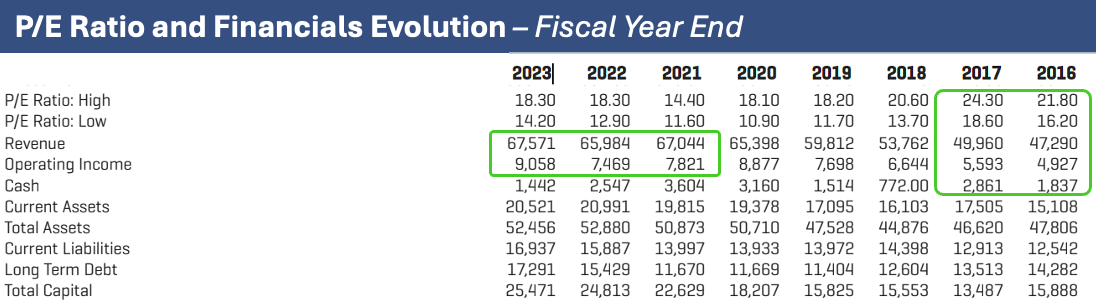
Lockheed Martin, a global aerospace and defense behemoth, derives nearly three-quarters of its substantial $67.6 billion 2023 revenue from the United States Department of Defense, the world’s largest military spender. The company is poised to oversee the largest defense procurement program in history, the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, well into the 2060s. This long-term, high-value contract, coupled with the company’s significant scale and diversified portfolio, makes Lockheed Martin a compelling investment for those seeking exposure to the defense industry.
Recent geopolitical tensions and increased defense spending have created a favorable environment for Lockheed Martin. The urgent need to resupply Ukraine’s depleted munitions stockpiles has provided a short-term boost, while the Pentagon’s long-term focus on modernizing its forces to counter rising threats from China and Russia offers sustained growth opportunities.
The global defense landscape is shifting. Nations like Germany and Japan are increasing their military budgets in response to geopolitical risks. This trend, combined with the United States’ sustained defense spending, creates a robust market for defense contractors.
While the defense industry faces challenges such as labor shortages and supply chain constraints, Lockheed Martin’s strong financial position, technological expertise, and strategic alignment with key defense priorities position it well to capitalize on future growth opportunities. As the world grapples with geopolitical uncertainty, Lockheed Martin remains a dominant force in the global defense industry.
Key Concerns:
A proposed "Department of Government Efficiency" (DOGE) under the Trump administration has raised concerns within the US defense sector. Led by figures like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, DOGE aims to reduce federal spending by a substantial margin. While budget cuts are not new to the defense industry, the potential for disruptive innovation and aggressive cost-cutting measures introduced by DOGE could pose significant challenges to traditional defense contractors.
Aggressive Cost-Cutting: DOGE's focus on reducing defense procurement costs could lead to increased competition, price pressure, and potential contract renegotiations.
Disruptive Innovation: Musk's track record of disrupting established industries suggests a potential for innovative approaches to defense contracting, which could challenge traditional business models.
Regulatory Changes: Streamlined regulations and reduced bureaucratic hurdles could accelerate the procurement process but may also increase competition and shorten contract cycles.
However, it's important to note:
Congressional Influence: Defense spending is heavily influenced by Congress, and bipartisan support for military modernization and increased budgets could mitigate the impact of DOGE's initiatives.
Complex Procurement Process: The complex nature of military procurement, with its stringent regulations and long-term contracts, may limit the scope of potential disruptions.
Industry Resilience: Major defense contractors like Lockheed Martin have strong financial positions, diversified portfolios, and long-term contracts, which could help them weather potential challenges.
While the potential impact of DOGE on the US defense sector remains uncertain, it is clear that the industry will need to adapt to a changing landscape. By focusing on innovation, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, defense contractors can position themselves to thrive in this new era.
Bullish Factors
Geopolitical Tailwinds: Rising geopolitical tensions, particularly the Russia-Ukraine war and Middle East conflicts, are driving increased defense spending, benefiting major contractors like Lockheed Martin.
Acyclical Business: The defense industry's acyclical nature provides a degree of protection against economic downturns.
Long-Term F-35 Revenue: Lockheed Martin's role as the prime contractor for the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, the largest defense program in history, ensures a steady revenue stream for decades to come.
Bearish Factors
F-35 Program Risks: Despite recent progress, the F-35 program continues to face operational challenges and potential funding risks, which could impact the company's financial performance.
Emerging Competition: Disruptive innovators like SpaceX and Anduril pose potential threats to Lockheed Martin's dominance in space and autonomous systems.
Political Risk: Lockheed Martin's significant reliance on US military funding exposes it to political uncertainties and budget cuts.
The following three tables and earnings report summary provide more context of fundamental facts (Return on Equity, Price/Sales, Net Income, Price/EBITDA, and more during the years), they’re analyzed in these fundamental publications providing academic explanations about when an indicator or financial item can be considered positive or negative for a company in different circumstances. BA, and GE follow with the same structure. A list of key additional competitors is also provided for each company.
Table 1 for LMT:
Two elements are worth highlighting from the first table: LMT presents consistent growth in Revenue and Operating Income.
Revenue growth is crucial for a company's long-term success and sustainability for several key reasons:
1. Profitability and Financial Health:
Increased Profit Potential: Revenue is the top line of the income statement. Growing revenue, while managing costs effectively, directly leads to higher profits. Increased profits can then be reinvested back into the business for further growth, distributed to shareholders as dividends, or used to pay down debt.
Covering Costs and Investments: Consistent revenue growth ensures the company can cover its operating expenses (salaries, rent, utilities, etc.), invest in research and development, upgrade technology, and expand into new markets. Without sufficient revenue, a company may struggle to maintain operations and remain competitive.
2. Attracting Investors and Capital:
Investor Confidence: Revenue growth is a primary indicator of a company's health and potential. Investors are more likely to invest in companies demonstrating consistent revenue growth, as it signals strong demand for their products or services and effective business strategies.
Higher Valuation: Companies with strong revenue growth are typically valued higher by the market. This increased valuation makes it easier for the company to raise capital through equity or debt financing, which can be used to fund further expansion and growth initiatives.
3. Market Share and Competitive Advantage:
Expanding Market Presence: Growing revenue often indicates that a company is gaining market share and outperforming its competitors. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as introducing new products, entering new markets, or improving marketing and sales efforts.
Competitive Edge: Revenue growth provides companies with the resources to invest in innovation, improve efficiency, and respond to changing market conditions. This allows them to maintain a competitive edge and stay ahead of the curve.
4. Long-Term Sustainability and Growth:
Reinvestment and Expansion: Consistent revenue growth enables companies to reinvest profits into the business, fueling further growth and expansion. This can create a virtuous cycle of growth, where increased revenue leads to more investment, which in turn leads to even greater revenue.
Adaptability and Resilience: Companies with growing revenue streams are better equipped to weather economic downturns, adapt to changing consumer preferences, and overcome unexpected challenges. They have more flexibility to adjust their strategies and operations as needed.
5. Employee Morale and Talent Acquisition:
Attracting and Retaining Talent: Successful, growing companies are more attractive to talented employees. They offer better career opportunities, job security, and potential for higher compensation.
Boosting Morale: Revenue growth can boost employee morale and motivation, as it demonstrates that the company is performing well and making progress towards its goals.
on the other hand, growth in operating income is a vital sign of a company's financial health and efficiency. It reveals how well a company is performing its core business operations, independent of financing and tax considerations. Here's why it's so important:
1. Core Business Performance:
Efficiency and Profitability: Operating income (also known as EBIT - Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) shows how much profit a company generates from its main business activities after deducting operating expenses like cost of goods sold (COGS), salaries, rent, marketing, and depreciation. Consistent growth in operating income indicates that the company is becoming more efficient at managing its costs and generating profits from its core operations.
Operational Effectiveness: It reflects how well the company manages its day-to-day operations. Growing operating income suggests effective cost control, efficient production processes, successful pricing strategies, and strong sales performance.
2. Sustainable Profitability:
Focus on Core Operations: Unlike net income, operating income excludes non-operating items like interest income/expense and taxes. This provides a clearer picture of the company's ability to generate profit from its primary business, making it a more reliable indicator of sustainable profitability.
Less Susceptible to Accounting Manipulation: Operating income is less prone to accounting manipulations compared to net income, which can be affected by one-time gains or losses, changes in tax rates, or financing decisions.
3. Comparison and Benchmarking:
Industry Comparisons: Operating income allows for better comparisons between companies within the same industry, as it removes the impact of different capital structures (debt vs. equity) and tax rates. This helps investors identify companies that are more efficient and profitable in their core operations.
Trend Analysis: Tracking operating income over time reveals valuable insights into a company's performance trends. Consistent growth indicates improving operational efficiency and profitability, while declining operating income may signal underlying problems.
4. Investment Decisions:
Attractiveness to Investors: Investors often use operating income as a key metric when evaluating investment opportunities. Companies with growing operating income are generally considered more attractive, as it indicates a healthy and well-managed business.
Valuation: Operating income is a crucial input in many valuation models, such as the discounted cash flow (DCF) model. Growing operating income translates to higher future cash flows, which in turn leads to a higher company valuation.
5. Financial Health and Stability:
Ability to Service Debt: A healthy and growing operating income provides companies with the financial capacity to service their debt obligations (interest payments).
Reinvestment and Growth: Growing operating income provides the resources necessary to reinvest in the business, fund research and development, expand operations, and pursue growth opportunities.
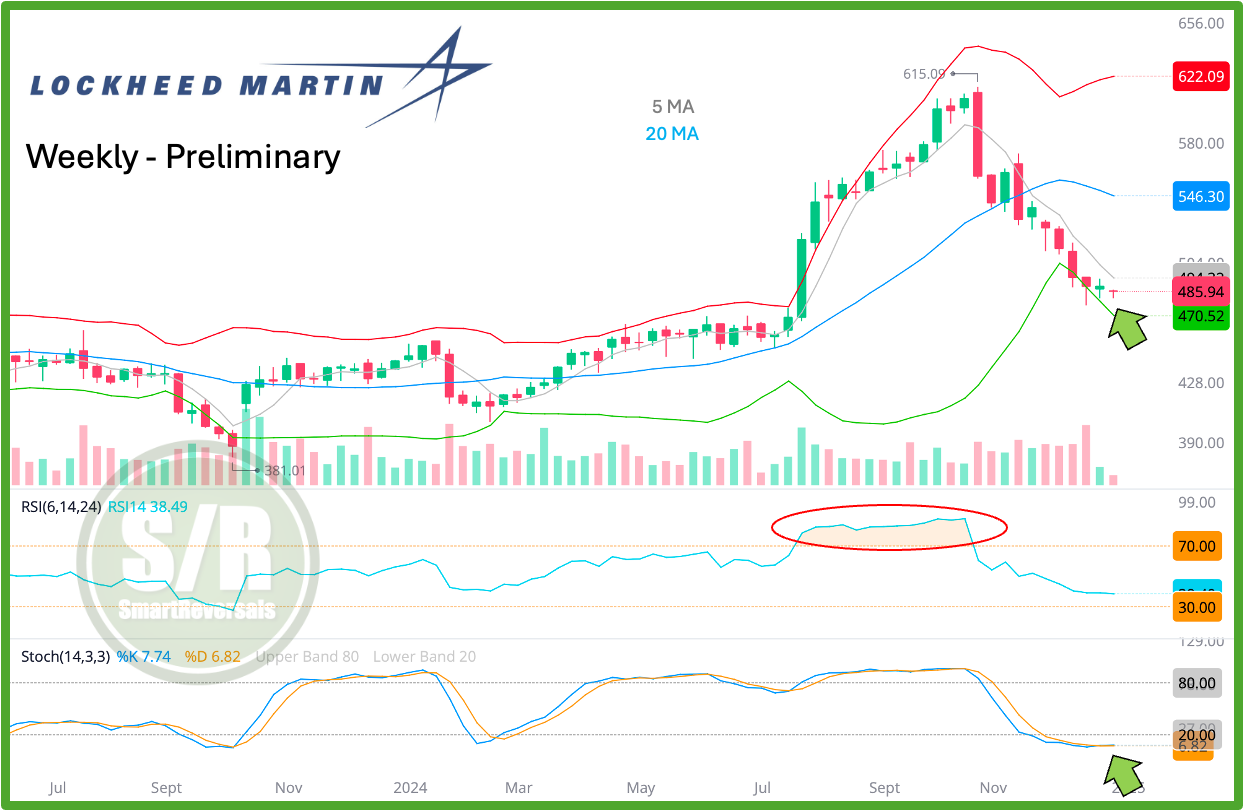
Technical Chart As of Dec 31st 2024:
Before continuing with fundamentals, let’s study the preliminary weekly chart based on yesterday’s close, price action is starting to show indecision at oversold levels relative tot he Stochastic, volume is drying and the lower Bollinger band was reached.
This is the weekly chart, so oversold levels are more meaningful than in a daily chart, risk reward is starting to favor bulls and $475 is a good reference to manage risk for longs in the very short term. For this week, a recovery of $488 would be positive to consider a bouncing process.
If a bounce occurs as the weekly chart is suggesting as of today, a flip to the 5MA from resistance to support would add more bullish factors to the reversal signals.
The cautionary element is brought by SPX, which is bearish so a continuation in the major indexes could affect a bounce for LMT.
Last but not least, observe the weekly RSI: The overextension lasted several weeks, but it came with a cost. Technicals don’t matter until they do. (Makes me think about PLTR, and makes me remember NVDA when it retraced more than 30% after the summer euphoria).
Tables 2 and 3: Growth and Fundamental indicators during the years: